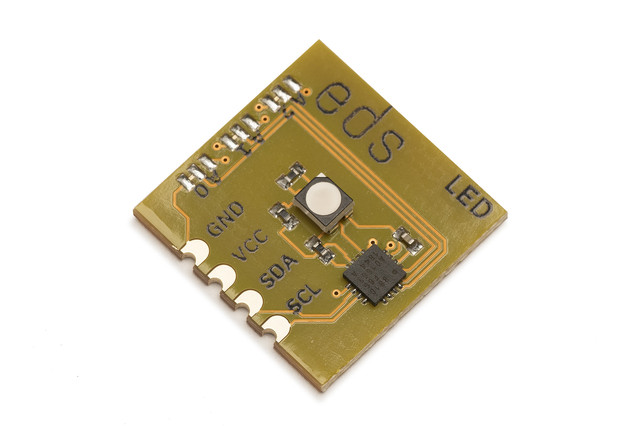
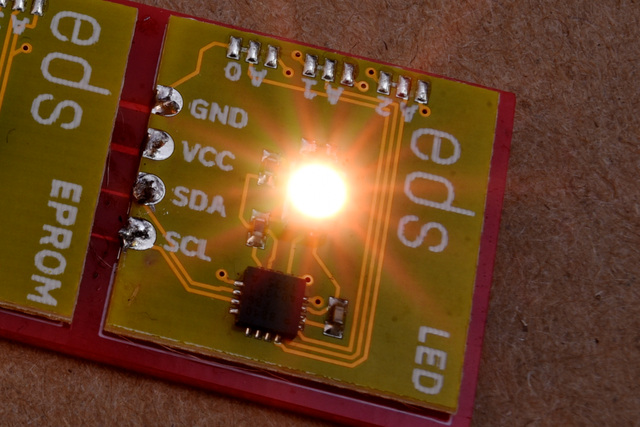
Electric Dollar Store
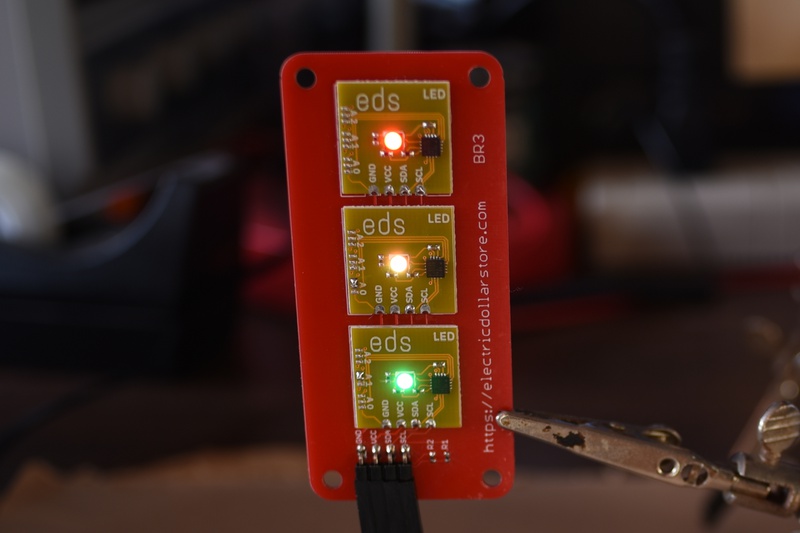
LED is a “Smart LED”, a bright LED emitter with color completely under software control. You can use it for indicators at low brightness and console lighting at full brightness. LED uses a bright, clear, flicker-free RGB LED that is controlled over I²C using a straightforward write-only protocol. Up to 8 LEDs can share an I²C bus under completely independent control.
LED uses 16-bit per channel high-speed PWM to drive each color channel. The output is gamma-corrected so that the increase in brightness s smooth over the entire 1-255 value range.
LED has two commands: an instantaneous "set color" command, which specifies the red, green and blue color byte values:
and a fade command for smooth color transitions:
where <time> is the fade duration in units of 1/30th of a second. For example 15 gives a fade time of a half second, and 60 gives a fade time of two seconds.
import sys
import serial
import time
import struct
import random
from i2cdriver import I2CDriver, EDS
if __name__ == '__main__':
i2 = I2CDriver(sys.argv[1])
d = EDS.LED(i2)
TEAL = 0x008080
ORANGE = 0xffa500
while 1:
time.sleep(1)
d.hex(TEAL, 3)
time.sleep(1)
d.hex(ORANGE, 3)
#include <Wire.h>
// Set the color to (r,g,b). Each is a byte 0-255.
// If t is nonzero, the change happens over t/30 seconds.
// For example if t is 15 the color fades over a half-second.
void led(byte r, byte g, byte b, byte t = 0)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(0x08);
Wire.write((t == 0) ? 0x00 : 0x01);
Wire.write(r);
Wire.write(g);
Wire.write(b);
if (t != 0)
Wire.write(t);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
// Set the color to hhh, a 24-bit RGB color.
// If t is nonzero, the change happens over t/30 seconds.
// For example if t is 15 the color fades over a half-second.
void led(uint32_t hhh, byte t = 0)
{
led(hhh >> 16, hhh >> 8, hhh, t);
}
#define TEAL 0x008080L
#define ORANGE 0xffa500L
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
}
void loop() {
delay(1000);
led(TEAL, 3);
delay(1000);
led(ORANGE, 3);
}
from machine import I2C
import time
class LED:
""" LED is an RGB LED """
def __init__(self, i2, a = 0x08):
self.i2 = i2
self.a = a
def rgb(self, r, g, b, t = 0):
"""
Set the color to (r,g,b). Each is a byte 0-255.
If t is nonzero, the change happens over t/30 seconds.
For example if t is 15 the color fades over a half-second.
"""
if t == 0:
self.i2.writeto(self.a, bytes((0, r, g, b)))
else:
self.i2.writeto(self.a, bytes((1, r, g, b, t)))
def hex(self, hhh, t = 0):
"""
Set the color to hhh, a 24-bit RGB color.
If t is nonzero, the change happens over t/30 seconds.
For example if t is 15 the color fades over a half-second.
"""
r = (hhh >> 16) & 0xff
g = (hhh >> 8) & 0xff
b = hhh & 0xff
self.rgb(r, g, b, t)
def main():
i2 = I2C(1, freq = 100000)
d = LED(i2)
TEAL = 0x008080
ORANGE = 0xffa500
while 1:
time.sleep(1)
d.hex(TEAL, 3)
time.sleep(1)
d.hex(ORANGE, 3)
| Default I²C address | 0x08 (0b0001000) |
| Current consumption (typ.) | 25 mA |
| Vcc | 3.3 V |