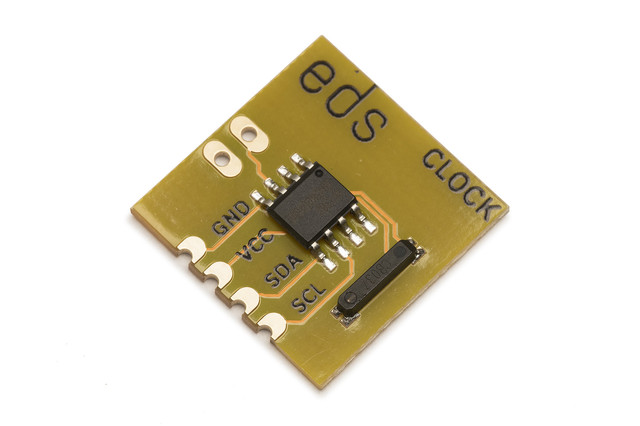
Electric Dollar Store
CLOCK is a real-time clock and calendar. There is an external connection for a backup battery. The HT1382 automatically switches to the battery supply when the VCC supply is lost. For additional precision, the HT1382 has a clock compensation control, which allows trimming the crystal frequency to within 1ppm.
import sys
import time
from i2cdriver import I2CDriver, EDS
if __name__ == '__main__':
i2 = I2CDriver(sys.argv[1])
d = EDS.Clock(i2)
d.set()
while 1:
print(d.read())
time.sleep(1)
#include <Wire.h>
class clock {
int a;
public:
int
year; // 2000 - 2099
byte
month, // 1 - 12
mday, // 1 - 31
hour, // 0 - 24
minute, // 0 - 60
second, // 0 - 60
weekday; // Day of week 1-7
void begin(byte _a = 0x68) {
a = _a;
}
byte bcd(byte x) {
return (x % 10) + 16 * (x / 10);
}
byte decimal(byte x) {
return (x & 0xf) + 10 * (x >> 4);
}
void set() {
Wire.beginTransmission(a);
Wire.write(7);
Wire.write(0);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(a);
Wire.write(0);
Wire.write(bcd(second));
Wire.write(bcd(minute));
Wire.write(0x80 | bcd(hour));
Wire.write(bcd(mday));
Wire.write(bcd(month));
Wire.write(weekday);
Wire.write(bcd(year % 100));
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void read() {
Wire.beginTransmission(a);
Wire.write(0);
Wire.endTransmission(false);
Wire.requestFrom(a, 7);
second = decimal(Wire.read());
minute = decimal(Wire.read());
hour = decimal(Wire.read() & 0x7f);
mday = decimal(Wire.read());
month = decimal(Wire.read());
weekday = decimal(Wire.read());
year = 2000 + decimal(Wire.read());
}
};
clock Clock;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Wire.begin();
Clock.begin();
Clock.year = 2019;
Clock.month = 4;
Clock.mday = 1;
Clock.hour = 8;
Clock.minute = 15;
Clock.second = 0;
Clock.set();
}
void loop() {
Clock.read();
Serial.print(" year:"); Serial.print(Clock.year);
Serial.print(" month:"); Serial.print(Clock.month);
Serial.print(" mday:"); Serial.print(Clock.mday);
Serial.print(" hour:"); Serial.print(Clock.hour);
Serial.print(" minute:"); Serial.print(Clock.minute);
Serial.print(" second:"); Serial.print(Clock.second);
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
from machine import I2C
import struct
import time
import utime
class Clock:
""" CLOCK is a HT1382 I2C/3-Wire Real Time Clock with a 32 kHz crystal """
def __init__(self, i2, a = 0x68):
self.i2 = i2
self.a = a
def set(self, tt = None):
""" tt is (year, month, mday, hour, minute, second, weekday, yearday), as used
by utime. """
if tt is None:
tt = utime.localtime()
(year, month, mday, hour, minute, second, weekday, yearday) = tt
def bcd(x):
return (x % 10) + 16 * (x // 10)
self.i2.writeto_mem(self.a, 7, bytes([0]))
self.i2.writeto_mem(self.a, 0, bytes([
bcd(second),
bcd(minute),
0x80 | bcd(hour), # use 24-hour mode
bcd(mday),
bcd(month),
1 + weekday,
bcd(year % 100)]))
def regrd(self, addr, fmt = "B"):
b = self.i2.readfrom_mem(self.a, addr, struct.calcsize(fmt))
return struct.unpack(fmt, b)
def read(self):
(ss,mm,hh,dd,MM,ww,yy) = self.regrd(0, "7B")
def dec(x):
return (x % 16) + 10 * (x // 16)
return (
2000 + dec(yy),
dec(MM),
dec(dd),
dec(hh & 0x7f),
dec(mm),
dec(ss),
dec(ww) - 1)
def main():
i2 = I2C(1, freq = 100000)
d = Clock(i2)
# Set the clock to 2010-2-10 14:45:00
d.set((2019, 2, 10, 14, 45, 0, 0, 1))
while True:
print('year=%4d month=%2d mday=%2d time=%02d:%02d:%02d weekday=%d' % d.read())
time.sleep(1)
| Default I²C address | 0x68 (0b1101000) |
| Current consumption (typ.) | 0.1 mA |
| Vcc | 2.8 - 5.5 V |